- 您现在的位置:买卖IC网 > Sheet目录225 > F1780DD20 (Curtis Industries)FILTER HI PERFORM 20A SCREW
�� �
�
 �
�Technical� Considerations�
�Meeting� Emissions� Standards�
�The� emissions� limits� that� a� piece� of� equipment� must�
�meet� will� depend� on� the� intended� market� for� that� piece�
�of� equipment.� If� there� is� more� than� one� market,� more�
�than� one� emission� standard� may� have� to� be� met.� This�
�can� have� a� substantial� effect� on� the� circuit,� size,� and� cost�
�of� a� filter.� Standards� like� the� CISPR’s� or� the� FCC� Rules�
�Part� 15� have� frequency� limits� of� 150� kHz� to� 30� MHz.�
�FCC� 15� AND� CISPR� CONDUCTED� EMISSION� LIMITS�
�DIGITAL� EQUIPMENT�
�(Line� Impedance� Stabilization� Network)� and� using�
�signal� generators� to� inject� RF� of� varying� amplitude� and�
�frequency,� some� insight� can� be� gained� as� to� the� nature�
�of� the� problem.� However,� the� criteria� for� acceptable�
�performance� will� have� to� be� decided� upon� so� that� a�
�filter� yielding� this� level� of� performance� can� be� obtained�
�from� the� test� procedure.� Unfortunately,� this� still� does� not�
�eliminate� the� need� for� final� testing� in� the� actual� operating�
�environment� which,� in� many� cases,� occurs� in� the� field.�
�Selection� of� a� suitable� filter� can� best� be� based� on�
�the� type� of� power� supply� or� input� impedance� of� the�
�equipment� and� on� the� mode� of� the� offending� RFI� noise.�
�80� –�
�78� –�
�Quasi-peak�
�Noise� Modes�
�dBμV�
�76� –�
�74� –�
�72� –�
�70� –�
�68� –�
�66� –�
�64� –�
�62� –�
�60� –�
�58� –�
�Average�
�Quasi-peak�
�Class� A� Industrial�
�Class� A� Industrial�
�Class� B�
�Residential�
�Power� line� filters� attenuate� noise� in� two� different� modes.�
�Common� Mode:� Also� known� as� line-to-ground� noise�
�measured� between� the� power� line� and� ground�
�potential.�
�Differential� Mode:� Also� known� as� line-to-line� noise�
�measured� between� the� lines� of� power.�
�Power� line� filters� are� designed� to� attenuate� either�
�one� or� both� modes� of� noise.� The� need� for� one� design�
�over� another� will� depend� on� the� magnitude� of� each�
�56� –�
�noise� type� present.� The� attenuation� is� measured� in� dB�
�54� –�
�52� –�
�50� –�
�48� –�
�46� –�
�Average�
�Class� B�
�Residential�
�(decibels)� at� various� frequencies� of� signal.�
�Circuit� Con� ?� guration�
�Power� line� RFI� filters� are� generally� built� with� two� or�
�0,15�
�0,5�
�Frequency� (MHz)�
�5�
�30�
�three-pole� filter� networks.� As� the� number� of� poles� and�
�the� corresponding� component� count� increases,� the�
�EMI� measurements� are� generally� made� using�
�Spectrum� Analyzers� with� Average� or� Quasi-Peak�
�detectors� in� accordance� with� methods� described�
�in� CISPR� 16.� Quasi-Peak� differs� from� Average�
�measurements� by� weight-averaging� the� peaks� into�
�the� total.�
�Equipment� meeting� these� specifications� can�
�utilize� a� filter� with� a� fairly� high� cutoff� frequency.� Other�
�standards� like� FCC� 18� with� a� low� frequency� limit� of� 10�
�kHz� will� result� in� the� equipment� using� lower� cutoff� filters.�
�As� might� be� expected,� the� lower� the� cutoff� frequency,�
�the� larger� the� physical� size� and� the� higher� the� cost� of�
�the� filter.�
�Conducted� RFI� Susceptibility�
�The� problem� of� susceptibility� can� be� extremely� difficult�
�to� deal� with� because� the� amplitude� and� frequency� of�
�the� offending� RF� noise� are� seldom� known� and� are� often�
�intermittent.� If� the� malfunction� can� be� duplicated� by�
�isolating� the� equipment� from� the� power� line� with� LISN’s�
�cost� will� increase� also.� Trying� to� typify� an� equipment’s�
�impedance� as� either� high� or� low� for� purposes� of� filter�
�selection� may� not� be� successful.� If� it� is� a� complex�
�impedance,� it� could� probably� be� low� at� some�
�frequencies,� high� at� others,� and� some� intermediate�
�value� at� still� other� frequencies.�
�Although� we� have� been� generally� successful� in�
�recommending� a� two-pole� network� for� linear� power�
�supplies� and� three-pole� networks� for� switching� power�
�supplies� and� synchronous� motors,� you� should� not� limit�
�your� testing� to� just� one� circuit� type� if� either� additional�
�circuit� performance� or� lower� cost� is� desired.� Consider�
�the� following:� If� the� equipment� looked� strictly� capacitive,�
�the� performance� of� a� two-pole� network� would� be�
�reduced� to� that� of� a� single-pole� filter.�
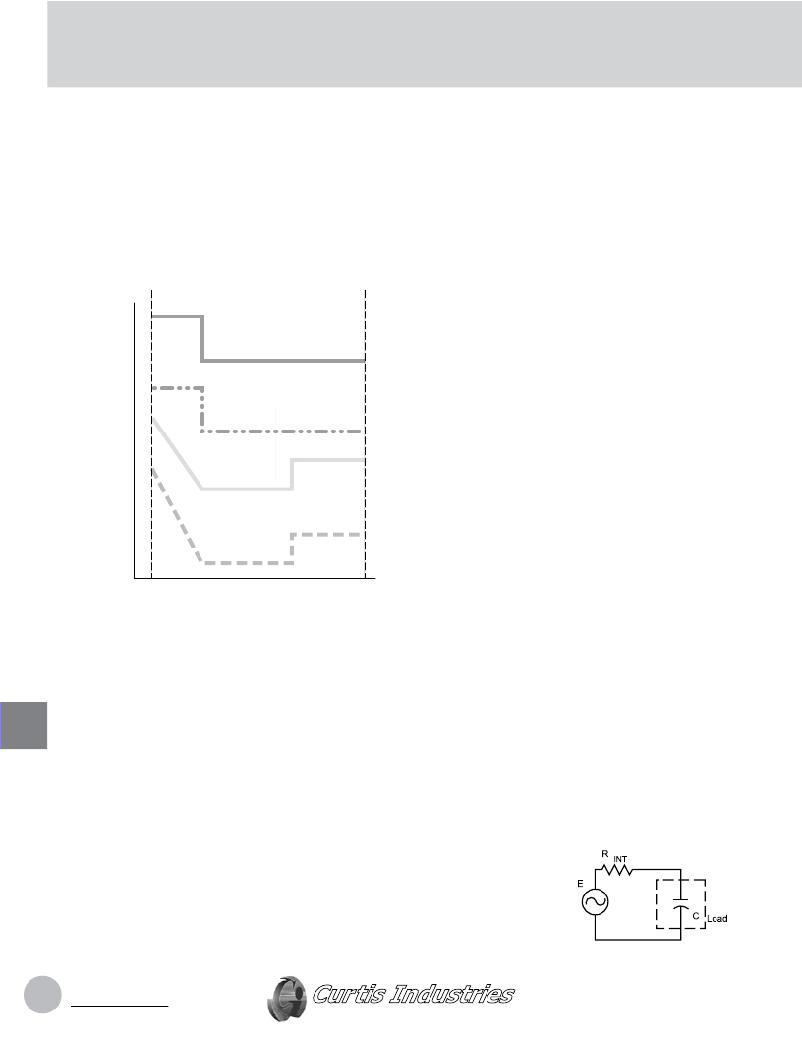
�Figure� 1a.�
�A� signal� source� (E)� with�
�its� internal� impedance�
�driving� a� capacitive� load.�
�86�
�www.curtisind.com�
�Curtis� Industries�
�A� Division� of� Powers� Holdings,� Inc.�
�发布紧急采购,3分钟左右您将得到回复。
相关PDF资料
F1799DD30
FILTER HI PERFORM 30A SCREW
F1900AA06
FILTER UL1410 6A FASTON
F2700AA03
POWER ENTRY FILTERED 3A FASTON
F2700AA06
POWER ENTRY FILTERED 6A FASTON
F2800BB15
FILTER HI PERFORM 15A WIRE
F3000AA06
FILTER POWER LINE MED 6A FASTON
F3099AA06
FILTER POWER LINE EMI 6A FASTON
F3480T112
FILTER 3-PHASE 480V 112A
相关代理商/技术参数
F17831-000
制造商:TE Connectivity 功能描述:VARISTOR 560V 5MM RADIAL 制造商:TE Connectivity 功能描述:VARISTOR 560V 400A DISC 5MM 制造商:TE CONNECTIVITY RAYCHEM-POLYSWITCH 功能描述:Var MOV 350VAC 460VDC 400A 560V Thru-Hole Bulk
F17833BR
制造商:Thomas & Betts 功能描述:PARTS - 10
F17834A
制造商:Thomas & Betts 功能描述:REPL GASKET,30A,MG,REC/NLT/CON
F17839A
制造商:Thomas & Betts 功能描述:REPL GASKET,60A,MG,REC/NLT/CON
F1788A
制造商:TE Connectivity 功能描述:
F1792EVBI
功能描述:VERSAMIXER EVAL BOARD 制造商:idt, integrated device technology inc 系列:- 零件状态:有效 类型:混频器 频率:400MHz ~ 3.8GHz 配套使用产品/相关产品:F1792 所含物品:板 标准包装:1
F1792NLGI
功能描述:RF Mixer IC 400MHz ~ 3.8GHz 24-TQFN (4x4) 制造商:idt, integrated device technology inc 系列:- 包装:托盘 零件状态:有效 RF 类型:- 频率:400MHz ~ 3.8GHz 混频器数:1 增益:11dB 噪声系数:10.7dB 辅助属性:- 电流 - 电源:147mA 电压 - 电源:3.3V 封装/外壳:24-VFQFN 裸露焊盘 供应商器件封装:24-TQFN(4x4) 标准包装:490
F17956-000
功能描述:可复位保险丝 240V .55A-HD 5.5A-MAX (R) RoHS:否 制造商:Bourns 电流额定值: 电阻:7.5 Ohms 最大直流电压: 保持电流:0.1 A 安装风格:SMD/SMT 端接类型:SMD/SMT 跳闸电流:0.6 A 引线间隔: 系列:MF-PSHT 工作温度范围:- 40 C to + 125 C